Within 500 s the surface of HNG1 HNG2 and HNG3 could be heated to an equilibrium temperature Fig. In this case it is said that the water vapor pressure over the liquid water is saturated.
Dynamic Nature Of Equilibrium Solid In Liquid Gas In Liquid Henry S Law
Supersaturation is a non-equilibrium condition in which some quantity of the macromolecule in excess of the solubility limit under specific chemical and physical conditions is nonetheless present in solution.

. Chemical tension in an alyzing the system equilibrium. The red-blue arrow is the reactive environment shift. Molecules escaping the liquid and that coming back becomes equal.
NRTL-HOC thermodynamic model is used for modeling the vapor-liquid and vapor-liquid-liquid equilibrium. Such situation is called by dynamic equilibrium between the escaping and returning molecules Fig. For components in suspension capillary interactions between drops of liquid with high interfacial free energy provide.
Established a novel growth model by assuming a two-dimensional island nucleation -growth process which is to the best of my knowledge currently the only model that can. Equilibrium is re-established by the formation and development of a solid state such as crystals as the saturation limit is attained. The choice of such a.
For components floating at a liquidliquid or liquidvapor interface the nature of the capillary interactions can be tailored by controlling the shape of the menisci at the interface between the components and the liquid. 8 the outlet fluid of the expander is superheated to at least 0 C for normal operation Kim and Perez-Blanco 2015. 98110 6 m s-1.
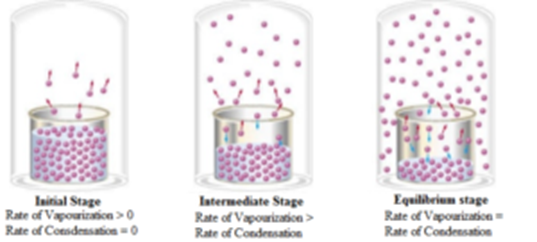
The relationship of permeability k to saturated hydraulic conductivity Ks is expressed as where ρ is the liquid density g the acceleration of gravity η the liquid dynamic viscosity Pa s and ρgη is termed the fluidity typical value for water at 20 is. This result has the same form as the well-known empirical relation μ A e B T displaystyle mu AeBT 2 where A displaystyle A and B displaystyle B are. Evaporation and condensation of water molecules in open and closed container.
The free energies of reactants and equilibrated conditions are calculated on the basis of the compositions shown in table S10. Note that k has dimensions of L 2. 1 where N A displaystyle N_A is the Avogadro constant h displaystyle h is the Planck constant V displaystyle V is the volume of a mole of liquid and T b displaystyle T_b is the normal boiling point.
7 the external fluids are all used for countercurrent heat transfer and undergo no phase change. A Nucleation-Growth Model of Nanowires Produced by the Vapor-Liquid-Solid Process PRAand AB. The reactions are catalyzed by using Amberlyst-15 catalyst.
There is a net transfer of one or more species from one liquid into another liquid phase generally from aqueous to. In this case three phases ice solid water liquid and vapor gas are in equilibrium with one another. The amount of liquid water will also remain constant if no vapor escapes from the system.
Each solid line is the boundary between two domains where two species are in equilibrium. Similarly equilibrium can also be established between the vapor phase and the liquid at a particular temperature. A liquid of suitable vapor pressure and viscosity range for transferring heat to or from a component for example a shelf or condenser in a freeze-dryer.
Based on thermodynamic properties and reaction kinetics this study presents three kinds of design alternatives for the overall RD system. The different linear dependence between the surface temperature and time represented a. The species with the lowest free energy is marked for each domain.
The outlet solutions of the absorber and generator are in a vapor-liquid equilibrium state. Liquidliquid extraction LLE also known as solvent extraction and partitioning is a method to separate compounds or metal complexes based on their relative solubilities in two different immiscible liquids usually water polar and an organic solvent non-polar. Two opposing processes such as evaporation and condensation that occur at the same rate and thus produce no net change in a system constitute a dynamic equilibriumIn the case of a liquid enclosed in a chamber the molecules continuously evaporate and condense but the amounts of liquid and vapor do not change with time.

Chemical Equilibrium Table Of Contents Dynamic Equilibrium Ppt Video Online Download

Liquid Vapor Equilibrium Ppt Download

Question Video Naming The Two Processes Which Establish A Constant Vapor Pressure When In Equilibrium Nagwa
0 Comments